Staking is the process of verifying transactions on a proof-of-stake blockchain in exchange for a reward. Unlike mining, which uses high-powered computers to solve complex mathematical equations, staking involves crypto holders locking up their crypto as collateral in a smart contract.
Through staking, holders can generate passive income without actively trading their coins. When you stake your coins, you are still in full possession of them – you are effectively sending them to work while you kick back.
Some of the most popular staking coins include ETH, ADA and SOL, but there are many, many more.
How does it work?
Validators (i.e. those who verify transactions) are selected based on the amount of cryptocurrency they have staked or locked up in the network. The more you stake, the higher the chances of selection. Selection is typically done in a random and algorithmic manner, depending on the specific consensus algorithm used by the blockchain network.
Got it… but how does this help secure the network?
Well, staked cryptocurrency serves as collateral. If a validator behaves maliciously, such as trying to double-spend coins or validate fraudulent transactions, they may lose their staked coins as a penalty. This gives them a financial incentive to act honestly and work in the best interest of the network – particularly for those who’ve staked a large sum.
Can anybody stake crypto?
Yes. While some blockchains require a minimum amount to become a fully-activated node (32 ETH in Ethereum’s case), many platforms offer staking pools that enable you to commit any amount of crypto in return for a shared reward.
Staking is a passive process that requires very little work, but you need to be able to find your way around exchanges to get started. Staking methods will depend on which platform and coin you select, but here’s a general overview.
(Keep reading for a description on how to stake on Binance.)
1. Choose a staking coin.
The first step is to choose a cryptocurrency that supports staking. The cryptocurrencies with the highest staking market cap are ETH, SOL and ADA, which typically yield around 4% to 5% annually. Tezos, Algorand and Polkadot are alternative staking options. Read here for more information on Tezos ‘baking‘ (staking), and here for more information on Algorand.
Each proof-of-stake blockchain has its own advantages: Cardano is eco-friendly, Solana offers fast, cheap transactions, and Ethereum has a first-mover advantage.
Note: If you stake Ethereum, you will not be able to withdraw until around mid-April, when the Shanghai upgrade goes live (assuming the upgrade is a success).
2. Obtain and store your coin in a secure wallet.
Next, you will need to obtain the staking coin by purchasing it from a cryptocurrency exchange or through a peer-to-peer transaction. Make sure to store your coins in a secure wallet that supports staking, such as Ledger or Binance.
3. Join a staking pool.
If it’s your first time staking, the easiest option is to join a staking pool. In a staking pool, holders pool together funds in order to increase the chance of becoming a validator and earning a reward. Some of the biggest staking pool platforms include Kraken, InfStones, SwissBorg, P2P, Stakefish, Blockdaemon and more.
There are a few things to consider when joining a staking pool.
- Size matters. The smaller the pool, the lower the chances of being selected as a validator, and vice versa. At the same time, large pools may bring lower rewards due to saturation.
- Is the pool reliable? If the staking pool has a history of server outages, you might want to reconsider. This is particularly true of the Solana blockchain, which is prone to outages.
- Fees. Staking pools take a small percentage of the rewards as a fee. 5% is an average fee, anything above 9 or 10% may be considered steep.
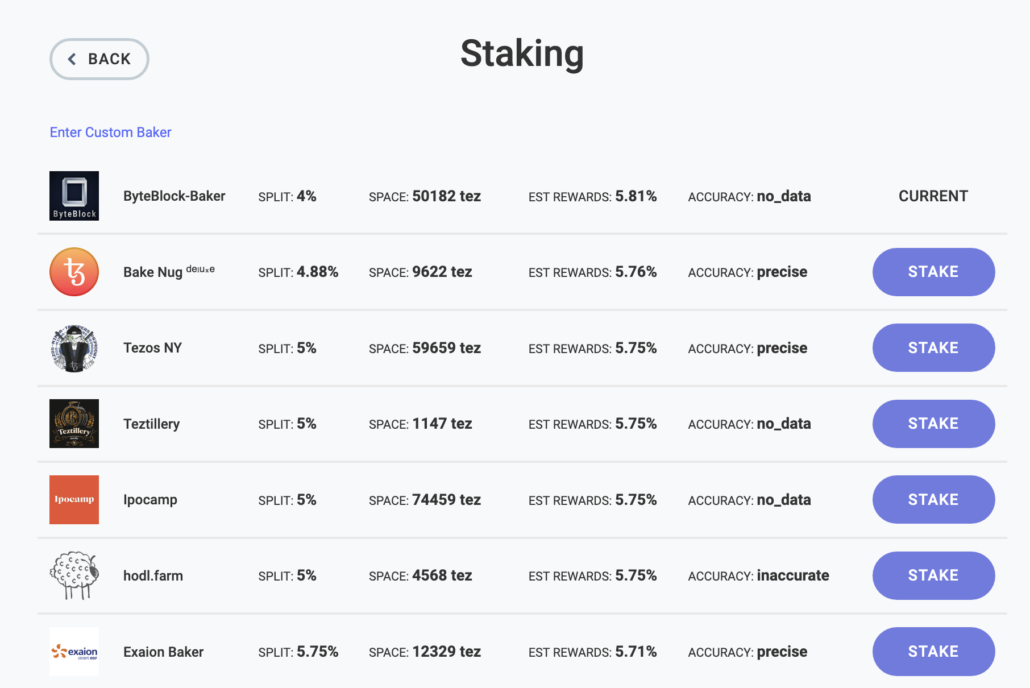
If you don’t want to join a staking pool, you can set up a node, which is essentially a dedicated server that communicates with the blockchain network. You can set up a node using a cloud-based service or by running your own hardware. Once your node is set up and running, you can stake your coins by locking them in a smart contract.
Read here to take a close look at what it’s like to be a fully-activated validator on Ethereum.
4. Validate transactions and earn rewards.
Once you have staked your coins, you can participate in the validation process and earn rewards for your contribution to the network. The amount of rewards you earn will depend on the amount of coins you have staked and the staking protocol you are using.
5. Keep an eye on your coins.
It’s important to monitor your staking regularly to ensure that your node is running smoothly and to stay informed about any changes to the staking protocol or network. You should also keep track of your rewards and make sure to withdraw them periodically to avoid any potential risks.

Staking on Binance
Binance is the largest cryptocurrency exchange by trading volume, and it’s a good place to start staking if it’s your first time.
Here’s a step-by-step on how to stake on Binance.
1. Create and verify a Binance account.
Opening a Binance account is simple, but you will need to provide official identification and proof of address to verify your account. Once that’s done, you can deposit your local currency to purchase the token you wish to stake. Remember that not every blockchain supports staking – you cannot stake Bitcoin or Dogecoin, for instance, since they validate via proof-of-work rather than proof-of-stake.
2. Select your staking protocol – fixed or locked?
Once your coins are in your Binance wallet, you can choose your staking protocol under the ‘Earn’ tab. Binance offers several staking options, including flexible staking and locked staking. Flexible staking allows you to withdraw your staked coins at any time, while locked staking requires you to commit your coins for a specific period in exchange for higher rewards. If you choose locked staking, you will need to select your staking term. Binance offers staking terms ranging from 7 to 90 days, with longer terms typically offering higher rewards.
If you explore the ‘Earn’ tab, you can find more staking options, such as ETH 2.0 staking and liquidity farming.
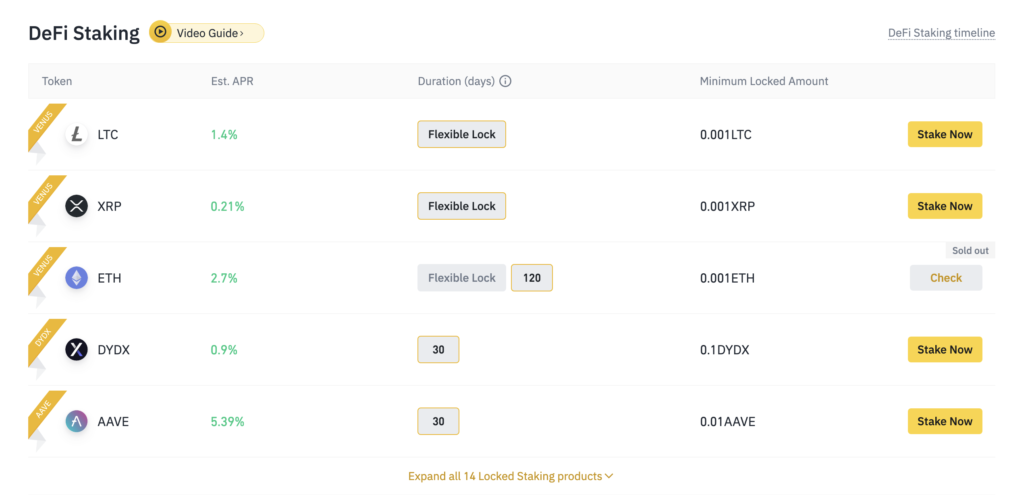
3. Confirm and monitor.
Double check your staking order and confirm. Once your staking order is confirmed, you can monitor your staking rewards in your Binance wallet. Binance will automatically distribute your rewards to your wallet on a regular basis, depending on the staking protocol and term you have chosen.
What are the benefits of staking?
Staking crypto is an easy way to earn passive income without having to actively trade your coins. This is particularly attractive to long-term investors who want to hold onto their coins for a longer period.
Staking is also extremely energy-efficient when compared with proof-of-work consensus mechanisms such as Bitcoin.
Other advantages include:
- Incentives for validators to act honestly.
- Increased scalability and security.
- Decreased risk of malicious actors.
- Easy, open-border options to participate in securing a decentralised network.
Are there downsides?
One of the main drawbacks is the potential risk of loss of funds. Validators may lose their staked cryptocurrency if they violate the rules of the network or fail to maintain their node (which is the whole point, after all).
While it’s easy to join a staking pool, becoming a fully-activated individual node can be expensive and difficult.

