Bitcoin is the first and most valuable cryptocurrency. Before we get into Bitcoin, we first need to know what a blockchain is. In its simplest form, a blockchain is a highly secure digital database or ledger that records permanent, uneditable transactions. This database is distributed across thousands of ‘nodes’ (i.e. computers) and is very difficult to hack.
There are four defining features of the Bitcoin blockchain.
1. It is peer-peer. This means that every transaction goes from computer A to computer B without a regulatory third party such as a bank. When you buy or send bitcoin to another user, your bank cannot see, block or control the transaction.
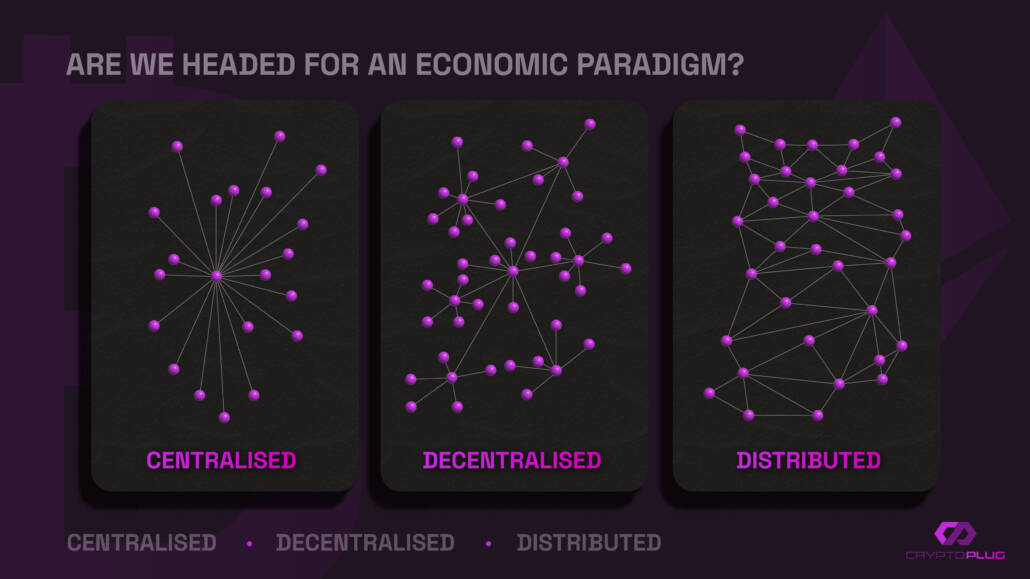
2. It is decentralised. While the traditional internet (i.e. ‘Web2’) operates through large centralised servers, the Bitcoin blockchain is distributed across roughly 10,000 ‘nodes’ (computers) that are connected to the Bitcoin network. This means that decision-making and control does not come down to one single individual or entity; power is distributed across the network. This structure also eliminates the possibility of a single point of failure.
3. It is immutable. All data recorded on the blockchain is permanent and cannot be changed. This means that blockchains are highly-secure, trustworthy and extremely difficult to hack.
4. It is public, meaning every transaction is viewable by the public and traceable by wallet address. In addition, Bitcoin is open-source, meaning anybody can view and propose changes to the code.
The first bitcoin was mined (i.e. added to the database) 14 years ago by Satoshi Nakamoto, an anonymous developer/group of developers. The goal of Bitcoin, outlined in the seminal whitepaper, is to enable individuals to transact directly with one another (i.e. peer-peer) without relying on the trust of a third party.
As a virtual currency, bitcoin is designed to act as money and a form of payment that functions outside the control of any one person or entity, such as banks and governments. It is also designed to prevent double spending – an issue that other digital currencies failed to tackle.
An increasing number of companies now accept bitcoin as a payment, including Wikipedia, Microsoft, AT&T, PayPal and more. Countries including El Salvador and the Central African Republic also accept bitcoin as legal tender.
Good to know
While Nakamoto founded Bitcoin, the idea for blockchain itself spans back several decades. In 1982, Berkeley PhD candidate David Chaum wrote a thesis theorising blockchain, titled “Computer Systems Established, Maintained, and Trusted by Mutually Suspicious Groups” – 27 years before Bitcoin.
Bitcoin has had a turbulent price history.
As a young, novel technology, the price of bitcoin has fluctuated to extremes over the years. The first bitcoin traded for $0.0008 in 2010, but by 2021, it soared in excess of $65,000. The price of bitcoin is likely to remain volatile until it’s fully regulated.
The supply of bitcoin is capped at 21,000,000. There are currently more than 19 million bitcoins in circulation – roughly 90% of the total supply. The supply of bitcoin is carefully controlled through the ”halving’ mechanism, whereby the block reward for miners is halved every four years, slowing the creation of new bitcoins. The next halving is in 2024. In line with the halving mechanism, the last bitcoin ever mined will be in 2140.
Many investors believe that bitcoin has the potential to hedge against the decreasing value fiat currency due to its fixed supply and trustless nature.
Unlike Ethereum, Bitcoin’s primary function is as a store of value, rather than supporting Dapps. The concept of blockchain technology itself, however, as conceived and popularised by Bitcoin, has many applications.
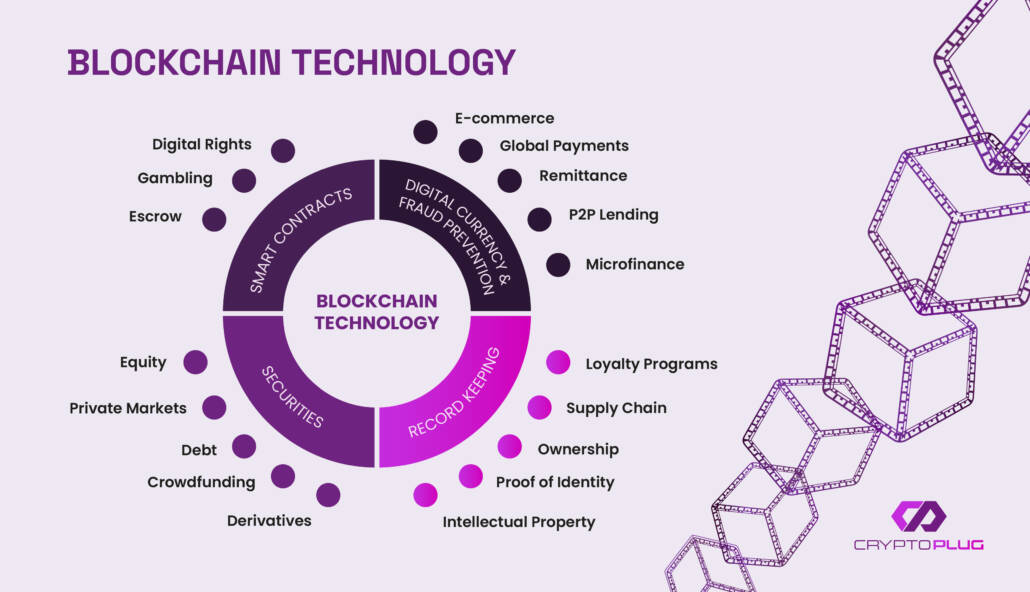
There are many companies now bridging the gap between blockchain technology and the traditional structures we all use today. Real estate marketplace Propy Inc offers properties that can be purchased through cryptocurrencies; Patientory uses blockchain to securely store medical records, and Mediachain uses smart contracts (a feature of Ethereum rather than Bitcoin) to give artists better, fairer streaming royalties.
Advantages of Bitcoin
- As a legacy currency, bitcoin is the most valuable and widely-known cryptocurrency with a very well established community of users. Although the price fluctuates, the algorithmic halving cycle does allow a small degree of predictability.
- The supply of bitcoin is fixed, so it has strong potential to hedge against inflation.
- The Bitcoin blockchain is incredibly secure and transparent. Transactions can never be edited or erased, and because the blockchain itself is stored across a large number of computers, a successful hacker would not be able access the entire chain.
Good to know
The first commercial bitcoin transaction was a Papa John’s pizza purchase in 2010. Unbelievably, Laszlo Hanyecz paid 10,000 BTC for the pizzas (roughly $41 at the time). 10,000 BTC today would be worth in excess of $500 million.
Disadvantages of Ethereum
- It’s very hard – often, impossible – to correct or recover any mistakes made during a transaction. Because of this, around 25% of all bitcoins are lost from misplaced passwords or lost hard drives.
- As a proof-of-work blockchain, mining bitcoin requires enormous computing power that consumes huge amounts of energy. In one year, Bitcoin consumes more energy than Argentina and the UAE, at 121.05 TWh. Bitcoin’s carbon footprint could be reduced through using renewable energy sources.
- Anonymity and lack of regulation can attract bad actors into the space. Illicit sites like Silk Road infamously used bitcoin as a method of transaction, and scams are common. This is something that applies to all cryptocurrencies and can be overcome with tighter regulations.
Where can I buy BTC?
Bitcoin is the largest cryptocurrency and is available to purchase on all major exchanges including Binance, Coinbase Pro, Kucoin, OKX, Kraken, Bybit and more. It’s also available on decentralised exchanges such as Uniswap. You can read a full list of exchanges that list bitcoin here.
To buy bitcoin, you will need to create an account on one of the listed exchanges. You will then need to verify your identity and deposit your local currency into your account to purchase the coin. You will also need a wallet that supports bitcoin, such as Binance, Coinbase, Crypto.com, Electrum, Mycelium, Ledger or Trezor.
If you purchase bitcoin through an exchange such as Binance, it will be automatically stored in your Binance wallet. If you purchase a large sum, it’s best to transfer your funds to a non-custodial cold wallet such as Ledger.
Our favourite bitcoin wallets are:
- Ledger Nano X (non-custodial, cold wallet)
- Mycelium (non-custodial, best for mobile use)
- Exodus (non-custodial, beginner-friendly)
